NOTES¶
Mathematical Principle of Convolution¶
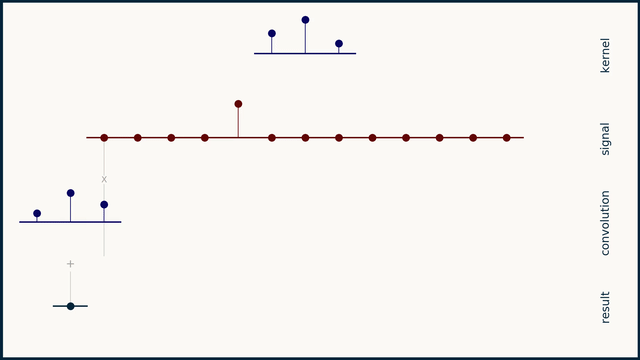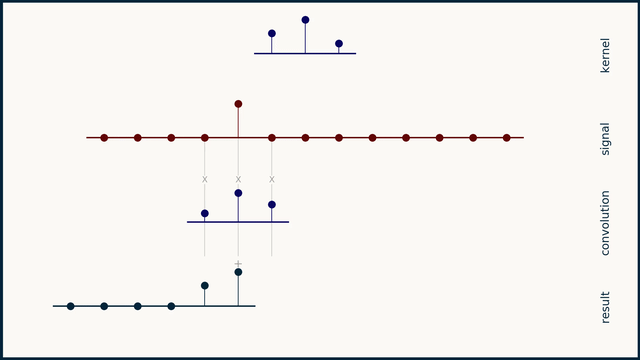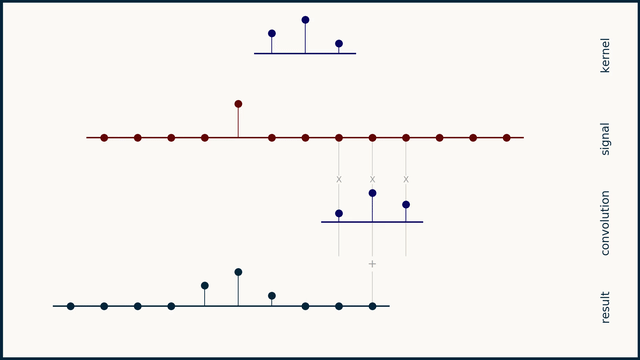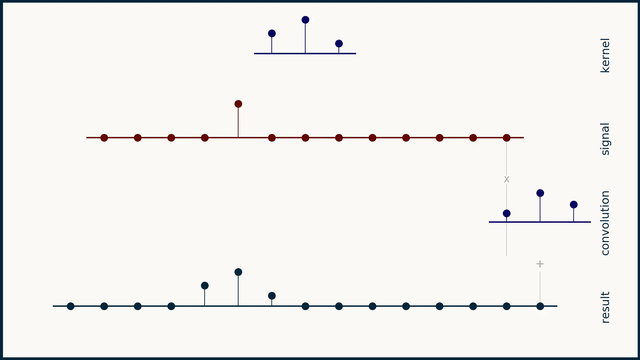
Convolution is an important operation in signal processing, which is used to describe the relationship between two signals. It can be regarded as the weighted average of one signal and another signal. The mathematical definition of convolution is as follows:
Where \(x(t)\) is the input signal, \(h(t)\) is the impulse response of the system, and \(y(t)\) is the output signal. The result of convolution is a new signal that contains all the information between the input signal and the impulse response of the system.
-
Physical Meaning of Convolution (Chinese)
Programming Philosophy¶
The convolution operation in this library actually reverses the direction of the convolution kernel and then multiplies it point by point with the input signal and sums it.
tiny_conv_f32¶
/**
* @name: tiny_conv_f32
* @brief Convolution function
*
* @param Signal The input signal array
* @param siglen The length of the input signal array
* @param Kernel The input kernel array
* @param kernlen The length of the input kernel array
* @param convout The output array for the convolution result
*
* @return tiny_error_t
*/
tiny_error_t tiny_conv_f32(const float *Signal, const int siglen, const float *Kernel, const int kernlen, float *convout)
{
if (NULL == Signal || NULL == Kernel || NULL == convout)
{
return TINY_ERR_DSP_NULL_POINTER;
}
if (siglen <= 0 || kernlen <= 0)
{
return TINY_ERR_DSP_INVALID_PARAM;
}
if (siglen < kernlen)
{
return TINY_ERR_DSP_INVALID_PARAM;
}
#if MCU_PLATFORM_SELECTED == MCU_PLATFORM_ESP32
// ESP32 DSP library
dsps_conv_f32(Signal, siglen, Kernel, kernlen, convout);
#else
float *sig = (float *)Signal;
float *kern = (float *)Kernel;
int lsig = siglen;
int lkern = kernlen;
// stage I
for (int n = 0; n < lkern; n++)
{
size_t k;
convout[n] = 0;
for (k = 0; k <= n; k++)
{
convout[n] += sig[k] * kern[n - k];
}
}
// stage II
for (int n = lkern; n < lsig; n++)
{
size_t kmin, kmax, k;
convout[n] = 0;
kmin = n - lkern + 1;
kmax = n;
for (k = kmin; k <= kmax; k++)
{
convout[n] += sig[k] * kern[n - k];
}
}
// stage III
for (int n = lsig; n < lsig + lkern - 1; n++)
{
size_t kmin, kmax, k;
convout[n] = 0;
kmin = n - lkern + 1;
kmax = lsig - 1;
for (k = kmin; k <= kmax; k++)
{
convout[n] += sig[k] * kern[n - k];
}
}
#endif
return TINY_OK;
}
Description:
This function performs the convolution operation between the input signal and the kernel. It first checks whether the input parameters are NULL, and then selects either the ESP32 DSP library or a standard C implementation for the convolution calculation based on the platform. The function returns the convolution result.
Features:
- Supports acceleration with the ESP32 DSP library.
- Supports swapping the signal and kernel to ensure the signal length is greater than the kernel length.
Parameters:
Signal: Input signal array.siglen: Length of the input signal array.Kernel: Input kernel array.kernlen: Length of the input kernel array.convout: Output array to store the convolution result.
Return Value:
TINY_OK: Convolution completed successfully.TINY_ERR_DSP_NULL_POINTER: One or more input parameters areNULL.
tiny_conv_ex_f32¶
/**
* @name: tiny_conv_ex_f32
* @brief Extended convolution function with padding and mode options
*
* @param Signal The input signal array
* @param siglen The length of the input signal array
* @param Kernel The input kernel array
* @param kernlen The length of the input kernel array
* @param convout The output array for the convolution result
* @param padding_mode Padding mode (zero, symmetric, periodic)
* @param conv_mode Convolution mode (full, head, center, tail)
*
* @return tiny_error_t
*/
tiny_error_t tiny_conv_ex_f32(const float *Signal, const int siglen,
const float *Kernel, const int kernlen,
float *convout,
tiny_padding_mode_t padding_mode,
tiny_conv_mode_t conv_mode)
{
if (NULL == Signal || NULL == Kernel || NULL == convout)
{
return TINY_ERR_DSP_NULL_POINTER;
}
if (siglen <= 0 || kernlen <= 0)
{
return TINY_ERR_DSP_INVALID_PARAM;
}
if (siglen < kernlen)
{
return TINY_ERR_DSP_INVALID_PARAM;
}
#if MCU_PLATFORM_SELECTED == MCU_PLATFORM_ESP32
if (padding_mode == TINY_PADDING_ZERO && conv_mode == TINY_CONV_FULL)
{
dsps_conv_f32(Signal, siglen, Kernel, kernlen, convout);
return TINY_OK;
}
#endif
int pad_len = kernlen - 1;
int padded_len = siglen + 2 * pad_len;
float *padded_signal = (float *)calloc(padded_len, sizeof(float));
if (padded_signal == NULL)
{
return TINY_ERR_DSP_MEMORY_ALLOC;
}
// Fill padded signal
switch (padding_mode)
{
case TINY_PADDING_ZERO:
// Middle copy only, left and right are zeros (calloc already zeroed)
memcpy(padded_signal + pad_len, Signal, sizeof(float) * siglen);
break;
case TINY_PADDING_SYMMETRIC:
for (int i = 0; i < pad_len; i++)
{
padded_signal[pad_len - 1 - i] = Signal[i]; // Mirror left
padded_signal[pad_len + siglen + i] = Signal[siglen - 1 - i]; // Mirror right
}
memcpy(padded_signal + pad_len, Signal, sizeof(float) * siglen); // Copy center
break;
case TINY_PADDING_PERIODIC:
for (int i = 0; i < pad_len; i++)
{
padded_signal[pad_len - 1 - i] = Signal[(siglen - pad_len + i) % siglen]; // Wrap left
padded_signal[pad_len + siglen + i] = Signal[i % siglen]; // Wrap right
}
memcpy(padded_signal + pad_len, Signal, sizeof(float) * siglen); // Copy center
break;
default:
free(padded_signal);
return TINY_ERR_DSP_INVALID_PARAM;
}
// Full convolution
int convlen_full = siglen + kernlen - 1;
for (int n = 0; n < convlen_full; n++)
{
float sum = 0.0f;
for (int k = 0; k < kernlen; k++)
{
sum += padded_signal[n + k] * Kernel[kernlen - 1 - k]; // Convolution is flip+slide
}
convout[n] = sum;
}
free(padded_signal);
// Handle output mode
if (conv_mode == TINY_CONV_FULL)
{
return TINY_OK;
}
else
{
int start_idx = 0;
int out_len = 0;
switch (conv_mode)
{
case TINY_CONV_HEAD:
start_idx = 0;
out_len = kernlen;
break;
case TINY_CONV_CENTER:
start_idx = (kernlen - 1) / 2;
out_len = siglen;
break;
case TINY_CONV_TAIL:
start_idx = siglen - 1;
out_len = kernlen;
break;
default:
return TINY_ERR_DSP_INVALID_MODE;
}
// Copy the selected part to the beginning
for (int i = 0; i < out_len; i++)
{
convout[i] = convout[start_idx + i];
}
}
return TINY_OK;
}
Description:
This function performs an extended convolution operation with options for padding and output mode. It first checks the input parameters and allocates memory for the padded signal. Depending on the selected padding mode, it fills the padded signal accordingly. The convolution is then performed, and the result is returned based on the specified output mode.
Features:
-
Supports different padding modes: zero, symmetric, periodic.
-
Supports different convolution modes: full, head, center, tail.
-
Handles memory allocation and deallocation for the padded signal.
Parameters:
-
Signal: Input signal array. -
siglen: Length of the input signal array. -
Kernel: Input kernel array. -
kernlen: Length of the input kernel array. -
convout: Output array for the convolution result. -
padding_mode: Padding mode (zero, symmetric, periodic). -
conv_mode: Convolution mode (full, head, center, tail).
Return Value:
-
TINY_OK: Convolution completed successfully. -
TINY_ERR_DSP_NULL_POINTER: One or more input parameters areNULL. -
TINY_ERR_DSP_INVALID_PARAM: Invalid parameters provided. -
TINY_ERR_DSP_MEMORY_ALLOC: Memory allocation failed.
Function Comparison¶
To help readers choose the appropriate function for their needs, here is a comparison between tiny_conv_f32 and tiny_conv_ex_f32:
| Feature | tiny_conv_f32 | tiny_conv_ex_f32 |
|---|---|---|
| Padding Mode | Zero padding only (implicit) | Zero, symmetric, or periodic padding (explicit) |
| Output Mode | Full convolution only | Full, head, center, or tail modes |
| Output Length | siglen + kernlen - 1 | Configurable based on conv_mode |
| Memory Usage | No dynamic allocation | Requires dynamic memory allocation for padded signal |
| Performance | Optimized (ESP32 hardware acceleration available) | Optimized only when using zero padding + full mode on ESP32 |
| Use Cases | Simple full convolution with zero padding | Advanced convolution with custom padding and output modes |
When to Use tiny_conv_f32¶
Use tiny_conv_f32 when:
-
You need a simple full convolution result
-
Zero padding is acceptable for boundary handling
-
You want maximum performance (especially on ESP32 with hardware acceleration)
-
You want to avoid dynamic memory allocation
-
The output length
siglen + kernlen - 1is acceptable
Example scenarios:
-
Basic signal filtering
-
Simple correlation operations
-
Real-time processing where memory allocation should be avoided
When to Use tiny_conv_ex_f32¶
Use tiny_conv_ex_f32 when: - You need different padding strategies (symmetric or periodic) to handle signal boundaries
-
You want to extract specific parts of the convolution result (head, center, or tail)
-
You need output length equal to input signal length (center mode)
-
You are processing signals where boundary effects matter (e.g., image processing, periodic signals)
-
You can tolerate dynamic memory allocation
Example scenarios:
-
Image filtering with symmetric padding to reduce boundary artifacts
-
Processing periodic signals with periodic padding
-
Extracting only the valid convolution region (center mode) when output length should match input
-
Advanced signal processing where boundary handling is critical